Can a Sinus Infection Cause Tooth Pain?
A sinus toothache is a dental pain caused by a sinus infection. This pain around the teeth is the result of the infection of the top sinuses, wherein the sinuses filled with fluid cause pressure on the area just above the back teeth, thus causing them to feel pain. It may also cause sensitivity in the upper back teeth when chewing or applying pressure on the said area of the teeth. [1]
Conversely, sinus infections can also result from dental sources, particularly an infection in the maxillary back teeth roots, which are located in the sinus cavity. Studies show that ten percent of all sinus infections are caused by a dental source. [2]
Jump Ahead
- What Is a Sinus Infection or Sinusitis?
- The Location of the Infected Sinus Determines the symptoms
- How to Determine If Sinus Infection Is Cause of Tooth Pain
- Glossary of Terms
- Expert Opinion
- Resources
What Is A Sinus Infection or Sinusitis?
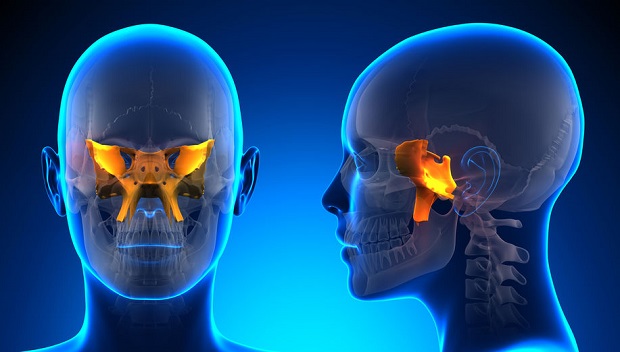
A sinus infection, also known as sinusitis, commonly refers to an acute bacterial infection of the sinus cavities. When sinus infections are caused by a bacterial infection, this leads to the collection of mucus in the sinuses, which become inflamed and congested. Bacterial sinus infections last for at least ten days. [3] Sinus infections can also be caused by allergies, chemical irritations, mechanical obstructions, or an infection in the maxillary tooth. [4]
The Location of the Infected Sinus Determines the Symptoms
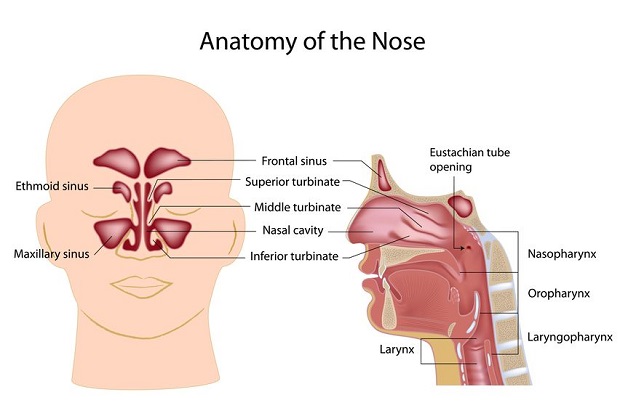
Four cavities known as paranasal sinuses can become infected to cause sinusitis. They all share a few common symptoms, but the pain associated with the infection is often limited to the infected sinuses’ location. For example, an infection in the frontal sinus will cause pain in the forehead where the sinus is located. An infection of the ethmoid will often cause pain around the eyes. The pain associated with the sphenoid sinuses could involve your neck and earaches. In the case of tooth pain, the sinus infection is likely to be in the maxillary sinus, which is located in the cheekbone. [5]
How to Determine if Sinus Infection is Cause of Tooth Pain

A sinus infection is not the only reason for dental pain; therefore, it is important for doctors to assess the history of the patient regarding sinus infections, perform exams on the dental bone to determine the source of the pain, and actually treat the sinus infection to either rule it out or conclude that it is the cause of the said tooth pain. [6]
Glossary of Terms

- Ethmoid Sinus: Sinus located just behind the bridge of the nose between the eyes.
- Frontal Sinus: Sinus located in the lower part of the forehead just above the brows.
- Maxillary Sinus: Sinus located just inside the cheekbone.
- Sphenoid Sinus: Sinus located behind the ethmoid sinus.
Expert Opinion

Quote: “In a way, the nerves that bring pain sensations from the sinus area and teeth to the brain — since they are all branches of the same nerve — are like my old bubble light string. Often you can’t immediately tell if the pain originated from a specific tooth or even from a sinus infection. We doctors make an educated guess based upon where the pain is most intense, what makes it worse, what makes it better, and any additional symptoms such as nasal congestion. In clear-cut cases the educated guess is accurate, and appropriate treatment is instituted. A person suffering from a dental infection is referred to a dentist. Pain from a sinus infection is cleared with an antibiotic and other medicines. In your case, however, the symptoms you reported and your doctor’s observations didn’t lead to a correct first guess. “
John C. Wolf, D.O.Associate Professor of Family Medicine Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine.
SINUS PAIN IS SOMETIMES THE RESULT OF A DENTAL PROBLEM
Resources
- [1][4] Jacobsen, Ph.D., DDS, Peter L., and Angelle M. Casagrande, DDS, MD., Dentistry Today – “Sinusitis As a Source of Dental Pain.”
- [2] Rogerson K., Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Knowledge Update, Microbiology of the Maxillary Antrum: Treatment of Infections, 1994, Volume: 1, pages: 49-59
- [3] American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery – “Sinusitis.“
- [5] National Institute of Allergies and Infectious Diseases – “What Are the Symptoms of Sinusitis?“
- [6] Peterson, Dr. Dan – “Sinus Headaches and Dental Health.”
DISCLAIMER: THIS WEBSITE DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE
The information, including but not limited to text, graphics, images, and other material on this website, is for informational purposes only. No material on this site is intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare providers with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment before undertaking a new healthcare regimen, and never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this or any other website.





