Does Beer Cause Gout?
According to one study, the answer is an emphatic yes.
- Drinking 2-4 beers per week increases gout risk by 25%.
- Drinking 2 beers per day increases gout risk by 200%
- The more beer you drink, the more likely you are to get gout.
An estimated 5 million Americans are known to have suffered from gout, a form of arthritis that typically occurs in overweight and middle-aged men. ((Singh JA, Sarkin A, Shieh M, Khanna D, Terkeltaub R, Lee SJ, Kavanaugh A, Hirsch JD. Health care utilization in patients with gout. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Jun;40(6):501-11.)) It is a type of rheumatic disease that often causes chronic and intermittent pain attacks in the wrist, hand, ankle, knee, and foot joints. It is caused by excess levels of uric acid that have been built up and formed into needle-like crystals in the joints, causing inflammation in the joints. ((American College of Rheumatology – Gout))
How Gout Develops
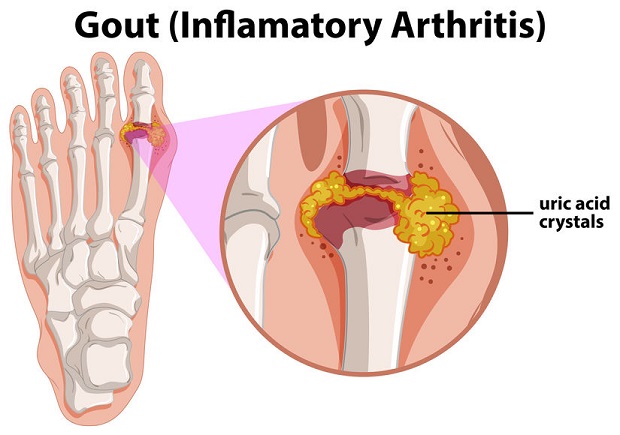
Once purines are processed in the body, it produces a waste product called uric acid. Typically, uric acid is removed through urination. However, high uric acid levels can form crystals and are deposited around the tendons and joints. This causes swelling, inflammation, stiffness, and chronic pain. ((Mayo Clinic – Gout Symptoms and Causes))
Gout and Alcohol Consumption

Although genetics have been linked to gout, there is no question that lifestyle plays a vital contributing factor. For instance, beer consumption has been associated with gout attacks for many years, but recent research studies have finally confirmed the association.
One compelling study conducted by Hyon K. Choi, MD, department of medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, followed more than 47,000 men over the course of twelve years. The study concluded that drinking as few as two to four beers a week increased the chance of gout by 25%. The men who drank two beers daily had an increased risk of gout by 200%. The more beer they drank, the more likely they were to suffer from gout, indicating that beer is directly related to gout. ((Choi HK, Atkinson K, Karlson EW, Willett W, Curhan G. Alcohol intake and risk of incident gout in men: a prospective study. Lancet. 2004;363:1277–81))
How Alcohol Increases the Risk of Gout Attacks
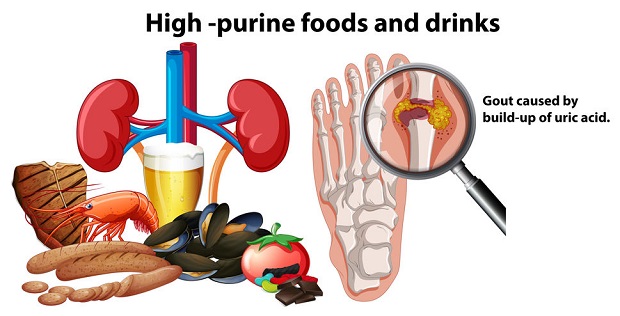
Individuals with gout are often advised to avoid foods and beverages with high purine levels, a substance that causes uric acid build-ups. High-purine foods may include fatty red meats, organ meats like liver, and specific types of seafood. High-purine beverages include all types of alcoholic beverages, and beer is at the top of the list. ((Mayo Clinic – Gout diet: What’s allowed, what’s not))
There are two ways that alcohol increases the risk of gout attacks:
- Alcohol inhibits uric acid removal in the body. Once it is metabolized in the body, it turns into lactic acid, which competes with the uric acid in the kidney during the elimination process or urination. This leads to high levels of uric acid retention in the body. ((Dandekar, Sucheta P, and Mahdi, Abbas Ali. Medical Biochemistry: Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates_2e-E-book. India, Elsevier Health Sciences, 2021.))
- Alcohol also contributes to increased levels of uric acid in the body. It increases the ATP levels in the body, converting into AMP – a substance that allows the easy buildup of uric acid in the body. ((Comprehensive Handbook of Alcohol Related Pathology. Netherlands, Elsevier Science, 2004.))
While indulgence in high-level purine foods and beverages are the main culprits of gout attacks, it is drinking alcoholic beverages (specifically beer) that seem to make a greater contribution. ((T. GIBSON, A. V. RODGERS, H. A. SIMMONDS, P. TOSELAND, BEER DRINKING AND ITS EFFECT ON URIC ACID, Rheumatology, Volume 23, Issue 3, August 1984, Pages 203–209))

