What Is Nitrogen?
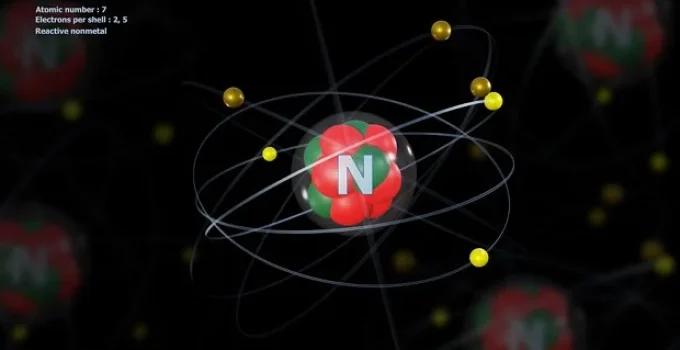
Nitrogen is a nonmetallic chemical element with the atomic number 7 and symbol N. It belongs to Group 15 of the periodic table (also known as the pnictogens) and plays a pivotal role in both biological systems and industrial chemistry. The nitrogen molecule (N₂) makes up approximately 78% of Earth’s atmosphere by volume, making it the most abundant uncombined element on Earth.
Despite this abundance, nitrogen in its elemental form is relatively unreactive due to the extremely stable triple bond (N≡N) between its atoms, which requires a great deal of energy to break.
Dive Deeper
- Where Is Nitrogen Found?
- The Chemical Properties of Nitrogen
- Common Nitrogen Compounds
- Why Nitrogen Matters
- 🎯 Final Thoughts
- 📚 References
Where Is Nitrogen Found?
Nitrogen is found in several natural and synthetic environments:
| Location | Form | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Earth’s atmosphere | N₂ (diatomic gas) | 78% of air by volume |
| Soil and fertilizers | Nitrates, ammonium | NH₄NO₃, KNO₃ |
| Biological tissues | Amino groups (-NH₂) | Proteins, DNA |
| Oceans and water systems | Dissolved nitrates | Nutrient cycles |
| Industrial environments | Liquid/gaseous N₂ | Welding, food preservation |
🔬 Interesting fact: The USGS estimates that over 120 million tons of nitrogen fertilizer are applied globally each year to enhance crop growth [1].
The Chemical Properties of Nitrogen
Chemically, nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and inert gas at room temperature. It exists as a diatomic molecule (N₂) with a very strong triple covalent bond, making it one of the most stable diatomic molecules in nature.
Key properties:
- Atomic number: 7
- Atomic mass: 14.007 u
- Electron configuration: 1s² 2s² 2p³
- Oxidation states: –3 to +5
- Electronegativity: 3.04 (Pauling scale)
Because of its bonding capabilities, nitrogen forms a variety of compounds, including ammonia (NH₃), nitric acid (HNO₃), nitrogen oxides (NO, NO₂), and organic amines.
🧪 Bond strength insight: The bond dissociation energy of the N≡N bond is about 945 kJ/mol, one of the highest known among diatomic molecules [2].
Common Nitrogen Compounds
Nitrogen is extremely versatile and forms compounds across a wide range of oxidation states. Some important categories include:
1. Ammonia (NH₃)
- Produced via the Haber-Bosch process
- Widely used in fertilizers, cleaning agents, and chemical synthesis
- Weak base, forms ammonium ion (NH₄⁺) in solution
2. Nitric Acid (HNO₃)
- Strong acid used in explosives, fertilizers, and nitration reactions
- Produced by the Ostwald process (oxidation of NH₃)
3. Nitrates (NO₃⁻) and Nitrites (NO₂⁻)
- Found in soil, fertilizers, and food preservatives
- Highly soluble and mobile in water, contributing to eutrophication in aquatic systems
4. Nitrogen Oxides (NO, NO₂, N₂O)
- Important in atmospheric chemistry and air pollution
- Nitrous oxide (N₂O) is also a greenhouse gas and anesthetic
Why Nitrogen Matters
Nitrogen plays a dual role in science and society: it is both essential for life and integral to industry.
🌱 Biological Importance
- A key element in amino acids, nucleotides, and proteins
- Participates in the nitrogen cycle, which moves nitrogen between atmosphere, soil, and organisms
🏭 Industrial Uses
- Ammonia synthesis for fertilizers (sustains global agriculture)
- Used as a coolant (liquid nitrogen) in cryogenics
- Protective atmosphere for manufacturing (e.g., in metallurgy and electronics)
- Preservation of food and biological samples
➤ Stat Snapshot: According to the FAO, nitrogen-based fertilizers are responsible for feeding over half of the world’s population through enhanced crop yields [3].
🎯 Final Thoughts
Nitrogen may be invisible and unreactive in its elemental form, but its chemical versatility and biological necessity make it a cornerstone of modern life. From the proteins in our bodies to the ammonia that fertilizes our crops, nitrogen’s fingerprints are everywhere. Understanding its chemical properties, reactions, and industrial applications offers a window into both nature’s balance and humanity’s ingenuity.
📚 References
- U.S. Geological Survey. (2023). Nitrogen Statistics and Information. https://www.usgs.gov
- Housecroft, C. E., & Sharpe, A. G. (2018). Inorganic Chemistry (5th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (2021). World fertilizer trends and outlook to 2022. https://www.fao.org/3/ca6746en/CA6746EN.pdf