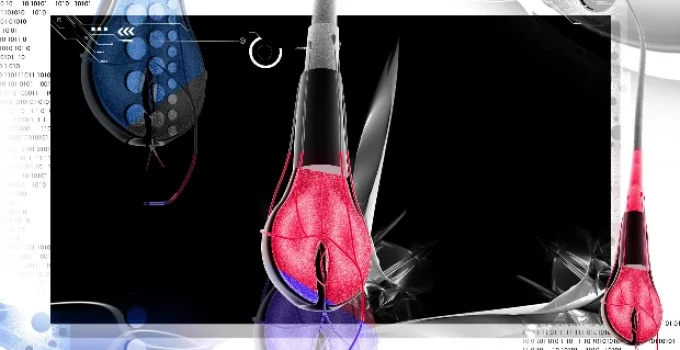
What Are Hair Follicles?
Have you ever wondered where your hair actually comes from? It doesn’t just sit on top of your skin—it grows from deep inside your body through tiny structures called hair follicles. These follicles are responsible for producing every single strand of hair on your body, from your eyebrows to your toes.
So, what are hair follicles exactly—and why are they so important to how your hair looks, grows, and even falls out?
Dive Deeper
- Where Are Hair Follicles Located?
- What Are the Parts of a Hair Follicle?
- How Do Hair Follicles Make Hair?
- What Affects How Hair Follicles Work?
- Do Hair Follicles Ever Go Away?
- 🎯Final Thoughts
- 📚 References
Where Are Hair Follicles Located?
Hair follicles are tiny, tube-like structures found in the dermis, the middle layer of your skin. Each one surrounds the root of a single hair. These follicles exist all over your body—except on the palms of your hands, soles of your feet, lips, and eyelids.
📊 Interesting Stat: The average person has more than 100,000 hair follicles on the scalp alone [1].
What Are the Parts of a Hair Follicle?
A hair follicle is more than just a hole in your skin. It has several important parts that help it grow and protect hair:
| Part of the Follicle | Function |
|---|---|
| Hair Bulb | The base where hair starts growing |
| Dermal Papilla | Supplies blood and nutrients to the bulb |
| Sebaceous (Oil) Gland | Releases oil to keep hair soft |
| Arrector Pili Muscle | Tiny muscle that causes “goosebumps” |
| Inner and Outer Sheath | Protects and shapes the growing hair |
🔍 Fun Fact: The arrector pili muscle contracts when you’re cold or scared, making your hair stand up and creating goosebumps! [2]
How Do Hair Follicles Make Hair?
Hair growth begins in the hair bulb, at the very bottom of the follicle. Cells in the bulb divide quickly and push upward. As they rise, they become filled with keratin, the same strong protein found in nails and skin. Eventually, these cells die and form the hair shaft, which is what you see growing out of your skin.
Hair grows in three phases:
- Anagen (Growth Phase): Lasts 2–7 years
- Catagen (Transition Phase): Lasts about 10 days
- Telogen (Resting Phase): Lasts 3–4 months before the hair falls out
Interesting Tidbit: On average, at any given time, ~90% of hair follicles are in anagen phase, 9% in telogen phase, and only 1% in catagen phase. [3]
What Affects How Hair Follicles Work?
Hair follicles are influenced by many internal and external factors, including:
- Genetics – Determines your hair type, thickness, and growth rate
- Hormones – Can speed up or slow down hair growth (especially during puberty)
- Nutrition – A healthy diet helps follicles produce strong hair
- Temperature – A study published in the Journal of British Dermatology found that seasonal changes affect hair growth to a small degree. [4]
- Damage or Pulling – Over-styling can stress follicles and slow growth
🧠 Science Tip: Follicles don’t just make hair—they’re part of your integumentary system, which includes skin and nails too!
Do Hair Follicles Ever Go Away?
Hair follicles are permanent structures in your skin. While they can become inactive (not growing hair), they usually stay in place unless they are destroyed by injury, burns, or certain medical treatments.
Even if you shave or wax, the follicle remains—which is why your hair grows back!
⏱️ Did You Know? About 50 to 100 hairs fall out every single day [5].
🎯Final Thoughts
So, what are hair follicles? They’re the small but powerful parts of your skin responsible for growing every hair on your body. Made up of special cells and surrounded by glands and tiny muscles, hair follicles play a key role in your body’s appearance, protection, and temperature control. Without them, we wouldn’t have eyebrows to keep sweat out of our eyes—or eyelashes to block dust and light.
Understanding hair follicles helps us appreciate just how much work goes on under the skin every day!
📚 References
📚National Institutes of Health. “Hair Follicles.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546248/
- Cleveland Clinic. “How Much Hair Loss Is Normal and When to Worry.”
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/how-much-hair-loss-is-normal - National Institutes of Health. “What Goosebumps Are For.” https://www.nih.gov/news-events/nih-research-matters/what-goosebumps-are
- Whiting DA. Male pattern hair loss: current understanding. Int J Dermatol. 1998;37(8):561–566. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-4362.1998.00542.x.
- Randall, V A, and F J Ebling. “Seasonal changes in human hair growth.” The British journal of dermatology vol. 124,2 (1991): 146-51. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1991.tb00423.x
- KidsHealth. “Your Hair.” https://kidshealth.org/en/kids/hair.html
📌Learn More About Hair
- What Causes Gray Hair✂The Science Behind Silver Strands
- Why Do People Have Different Hair Colors✂The Genetics Behind Every Shade
- What Causes Hair to Stand Up (Goosebumps!) ✂The Body’s Chilly Reflex Explained
- Why Does Hair Fall Out✂The Science Behind Shedding Strands
- What Is Human Hair Made Of✂The Surprising Science Behind Every Strand